In the ever-evolving world of lighting, two technologies continue to spark comparison: High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lighting and Light Emitting Diodes (LED). While both offer powerful illumination, they differ significantly in design, efficiency, and longevity. One of the most critical aspects of comparison between HID vs LED is lumen intensity, the measurement of visible light output. In this article, we’ll explore how lumen intensity is measured, maintained, and compared across these technologies to help you understand which is best suited for your commercial lighting needs.
Understanding the Core Differences
At a fundamental level, HID lighting operates by sending an electric arc between tungsten electrodes housed inside a gas-filled bulb. This interaction produces bright light but also generates significant heat and UV radiation. LED lighting, on the other hand, uses semiconductive materials to emit light when current passes through. LEDs are solid-state devices with directional light output, minimal heat, and excellent energy efficiency.
Beyond the structural differences, the way these lighting types handle lumens, their brightness over time, reveals a deeper contrast in performance.
What Are Lumens and Why Do They Matter?
Lumens measure the amount of visible light emitted by a source. More lumens mean a brighter light. However, not all lighting technologies maintain their brightness the same way or for the same duration. Understanding how lumen intensity is measured and how it declines over time is essential when evaluating HID vs LED lighting.
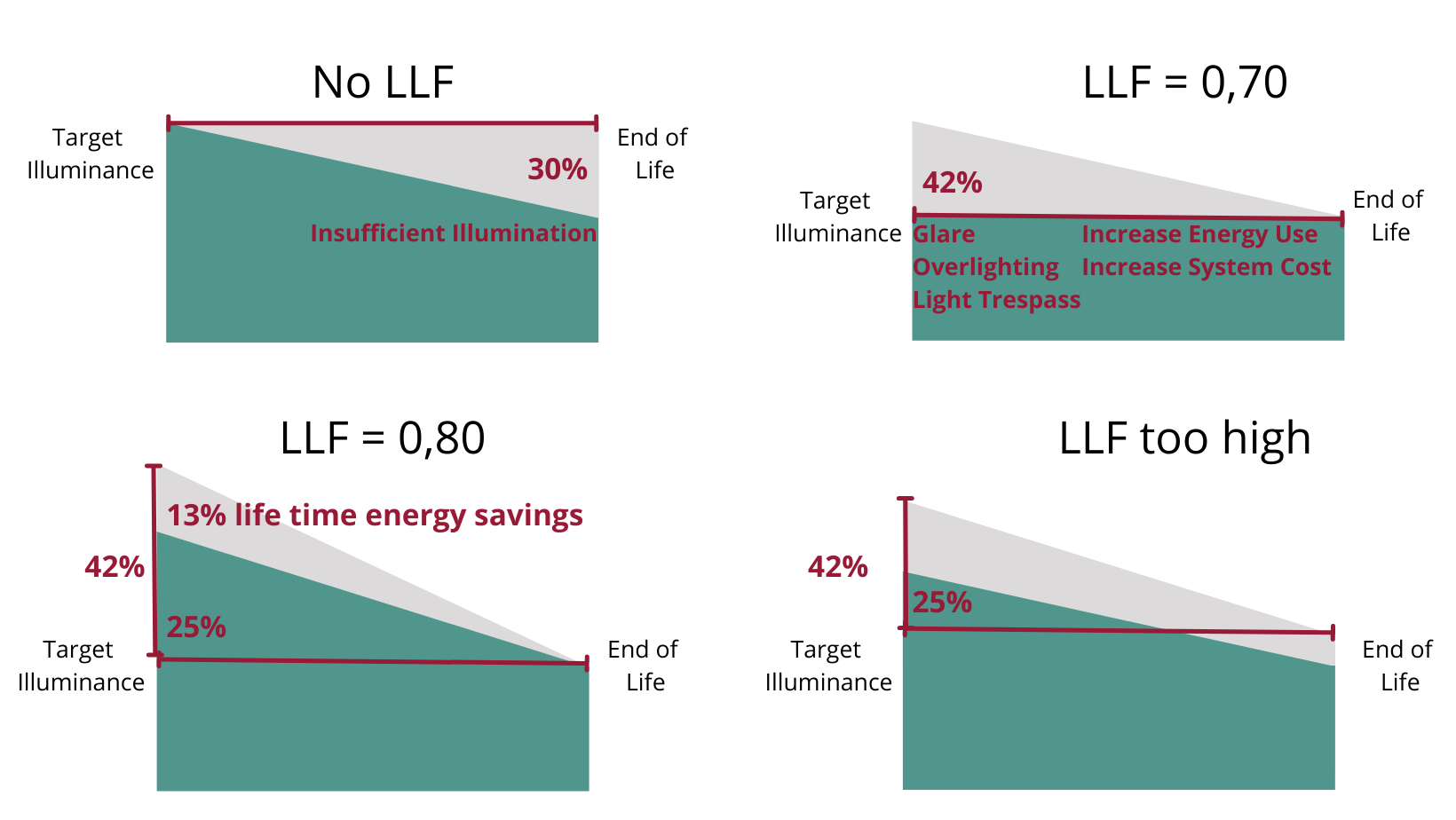
Initial Lumens: When Light Output Is at Its Peak
The concept of initial lumens refers to the maximum brightness emitted when a light source is first turned on. However, measurement timing differs by technology:
- LED Lighting: Lumen output is typically measured after about 45 minutes, once the diodes stabilize.
- HID Lighting: Lumen output is only measured after approximately 1,000 hours of usage during a process known as “burn-in.”
This discrepancy matters because early HID measurements might not reflect the actual usable light levels during regular operation, while LED measurements offer a more immediate snapshot of performance.
Lumen Maintenance and Decline Over Time
No light stays at its peak brightness forever. Over time, light intensity diminishes—a concept known as lumen maintenance. This degradation directly impacts how effective a lighting system remains as it ages.
For LED systems, lumen maintenance is tracked using industry-standard metrics:
- L90, L70, L50: These designations refer to the number of hours before an LED emits 90%, 70%, or 50% of its original light output. For example, an LED rated L70 at 72,000 hours means it will emit 70% of its initial lumens after 72,000 hours.
In HID lighting, lumen depreciation is more severe. Some HID lamps can lose up to 70% of their light output in as little as 10,000 hours. This steep decline not only affects visual comfort but also means increased maintenance and more frequent replacements.
Retailers need to pay special attention to the color rendering index, especially R9. What is R9 and why do you need to take it into consideration. It effects they way your eyes perceive color. You can learn more about color rendering index R9 here.
Absolute (Delivered) Lumens: Accounting for Real-World Performance
Absolute lumens, also referred to as delivered lumens, measure how much light actually reaches the intended area. This metric accounts for system inefficiencies such as heat loss, optical barriers, and fixture design.
- HID Lighting: Measured primarily by lamp output. Optical loss is typically not factored in, resulting in a less accurate representation of real-world performance.
- LED Lighting: The luminaire is tested as a whole, factoring in optical loss and providing a more precise account of usable light.
This distinction is important when comparing HID vs LED systems for applications like parking lots, warehouses, and street lighting—spaces where every lumen matters.
Why LEDs Outshine HID in Lumen Efficiency
While HID lights often have high source efficiency (lumens per watt), system efficiency tells a different story. Due to omnidirectional output and the need for reflectors and diffusers, HID systems lose a significant portion of usable light. In contrast, LED lights are directional, focusing their output where it’s needed, with minimal losses.
LED systems also maintain brightness longer, operate cooler, and are not plagued by flickering or cycling near end-of-life. Their higher system efficiency often results in greater energy savings and reduced lighting maintenance costs over time.
Conclusion: The Better Brightness Over Time
When it comes to choosing between HID vs LED lighting, lumen intensity, both in initial output and over the system’s lifetime, is a major deciding factor. HID lights may offer strong initial brightness, but their rapid lumen depreciation and higher maintenance needs make them less desirable for long-term use. LEDs, with their high lumen maintenance, accurate measurement of delivered lumens, and longer life span, deliver a brighter, more cost-effective solution in nearly every scenario.
Whether you’re upgrading an industrial facility, a parking garage, or a stadium, LED lighting provides a clear advantage in terms of brightness, efficiency, and sustainability. Want to learn which LED lighting products are best for your facility? Contact Action Services Group at 610-558-9773, email [email protected], or click the button below to speak with a lighting expert today.








































0 Comments